What Is Precision™ UAN?
Precision™ UAN is a high analysis nitrogen, liquid nitrogen fertilizer manufactured in Australia by Orica. It has a total N concentration of 40% w/v; containing 0.4 units of N/l . It offers extremely high efficiency compared to solid Urea, due to the fact it contains three nitrogen compounds as opposed to just one.
Being a true liquid formulation that is 100% stable, Precision™ UAN offers great versatility and safety with handling, storage and application. It is compatible with many chemicals, minerals and nutrients and can be applied through standard spray nozzles, allowing for greater operational efficiency.
The Urea Ammonium Nitrate (UAN) formulation makes this fertilizer one for all seasons. It’s a versatile source of nitrogen nutrition for all crop & pasture types and will enhance any farm fertilizer program.
Some of the key benefits of Precision™ UAN include:
- Maximizes feed quantity and quality; higher dry matter, protein and metabolizable energy levels with better digestibility.
- Has a positive impact on soil PH and benefits overall soil health.
- Works well in dry or cold conditions when urea is ineffective.
- Is readily available to the plant as applied, without the need of being hydrolyzed or converted by soil microbes.
- Minimal environmental N loss.
How Does UAN Compare With Urea?
To be able to directly compare Urea with Precision™ UAN, first we need to understand nitrogen in general and the process Urea goes through to become available to the plant. Below is a basic overview on why plants need N, the different forms of N, how they are utilized by the plant and how Urea works.
The Role Of Nitrogen In Plant Growth
Nitrogen is widely considered as the most important element for plant growth and development. It is a fundamental component of chlorophyll, the green pigment that enables plants to photosynthesize and convert sunlight into energy. Nitrogen is also a crucial building block for amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are essential for plant structure and function. Without an adequate supply of nitrogen, plants would exhibit stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and overall poor health. Overall, nitrogen is indispensable for plants to thrive and fulfill their biological functions, making it the most critical element for their survival and success.
Understanding N Forms And How They Are Utilized
Nitrogen (N) constantly cycles among different forms in the environment and can be a complex process to understand. To keep it simple there are 3 forms of Nitrogen typically found in fertilizers. These are: nitrate (NO3-), ammonium (NH4+), and urea (CO(NH2)2). Nitrate and ammonium are the only forms considered to be plant-available.
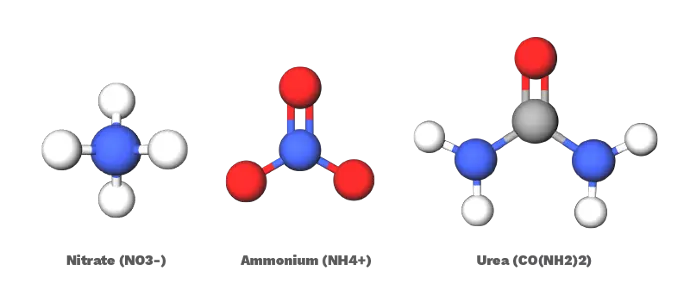
Nitrate nitrogen is a highly soluble form of nitrogen that is readily available for plant uptake. It is the most preferred form of nitrogen and is used by plants more than ammonium. It dose not need to go through physical change to be absorbed by the plant. It is a stable form of nitrogen and does not volatilize.
Ammonium is another form of nitrogen that is also easily absorbed by plants. It is largely retained on the soil cation exchange sites and is not easily leached and can also be converted into nitrate by soil micro-organisms. Ammonium is susceptible to volatilization; this is when it converts from ammonium to ammonia.
Urea is a form of nitrogen that cannot be utilized by a plant in its current state. Its is typically applied in a solid state which means it must first dissolve and then hydrolyze to ammonium before it becomes nutritious to the plant. Both these process depend heavily on rainfall or irrigation and the right temperature to work successfully.
What Is Urea And How Is It Used By Plants?
Urea is a type of nitrogen fertilizer used to provide plants with the essential nutrient nitrogen. It is a white, crystalline solid about 46% nitrogen, making it one of the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizers available. However, being the most concentrate form of N doesn't mean its the most effective. Urea as a form of nitrogen is not in a state that can be used by a plant. There a two things that must happen before it is available for plant uptake. One, it must dissolve and two, it must hydrolyze. The process of hydrolysis (the process of it changing from urea to ammonium) occurs when urea reacts with water and the soil enzyme urease. Urease is found in the soil and plant foliage. How quickly hydrolysis occurs depends on how active the urease enzyme is. Urease is less active as the temperature gets colder, therefore making Urea ineffective in cold temperatures. Once urea has hydrolyzed it is then in a form the plant can use.
So How Does Precision™ UAN Compere With Urea?
As we can conclude from above, not all nitrogen is created equal so to compere Precision™ UAN to Urea, based on N content is unintelligent. To get a more accurate comparison we must look at the types of N within each product and the NUE (Nitrogen use efficiency). There are many ways to measure NUE and each have their pro's and con's. You can see more in this article about Nitrogen Use Efficiency Definitions.
The below table is a side by side comparison of the nitrogen content in Precision™ UAN and Urea.
Nitrogen Content Type | Precision™ UAN (40% w/v) NPK (40-0-0) | Urea 46% NPK (46-0-0) |
Nitrate (NO3-) | 25% | 0% |
Ammonium (NH4+) | 25% | 0% |
Urea (CO(NH2)2) | 50% | 100% |
Plant Ready N Content* | 50% | 0% |
*Plant ready nitrogen is the nitrogen that can be utilized by the plant immediately.
Field Trial - Precision™ UAN to Urea Comparison
To compare Urea And Precision™ UAN we carried out a trial on a working dairy farm in North Taranaki that was a traditional user of Urea. It was located in a moderate climate with medium to high rainfall; conditions which are favorable to excellent Urea response.
Nitrogen was applied every grazing rotation (average of 32 days) over 9 months; April - December. In plot 1 Urea (SustaiN®) was applied at 80kg/Ha (36.8 Units of N). In plot 2 Precision™ UAN was applied at 25L/ha (10 Units of N). Feed weights and DM were measured at each grazing and the below graph is an average representation of the trial period.
Thorough pasture profiles were conducted by Hill Labs before during and after the trial and a few other stand out benefits included:
- The pH of plot 2 (Precision™ UAN) increased from 5.7 to 5.8 - The pH of plot 1 (Urea) fell from 5.7 to 5.6
- The leaf nitrate level in plot 2 (Precision™ UAN) was 30 - 40% less at time of grazing than that of plot 1 (Urea)
- The DM of plot 2 (Precision™ UAN) was consistently higher 1.5 - 6% than that of plot 1 (Urea)
*Based on Precision™ UAN at $2.52/L (NZD) and Urea at $944.00/ Ton (NZD).
Precision™ UAN is available here. Or if you require more info or have any question feel free to contact us.